G3 ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING | Your Ideas to Reality
G3 ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING | Your Ideas to Reality
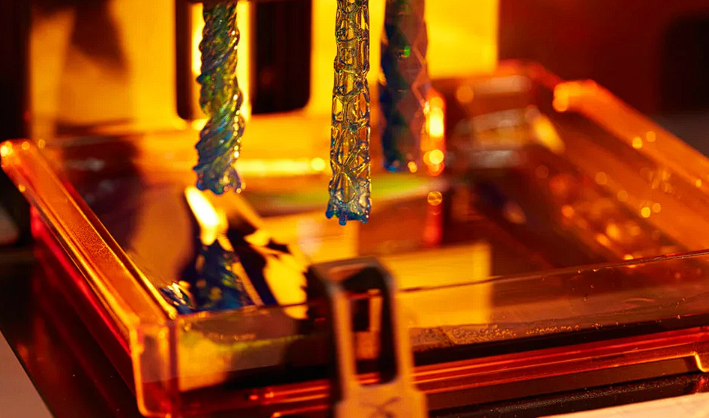

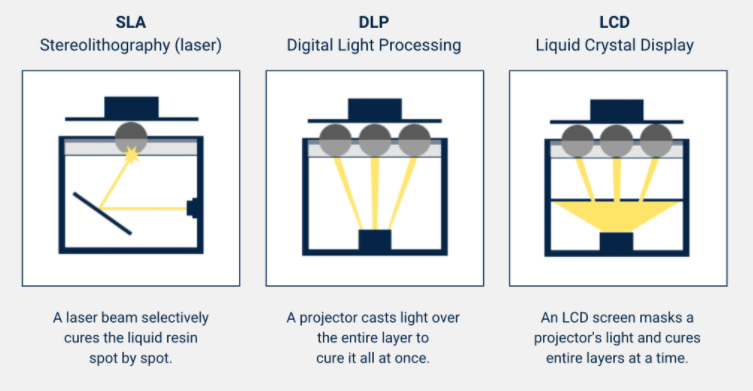
Resin 3D printing, also known as stereolithography (SLA), digital light processing (DLP), or liquid crystal display (LCD) 3D printing, is a type of 3D printing technology that uses a liquid photopolymer resin as the raw material.
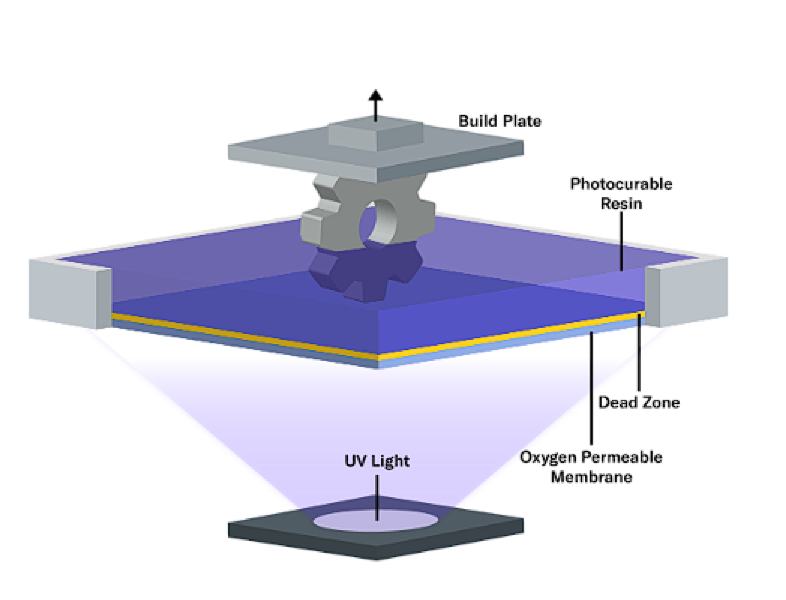
In resin 3D printing, a 3D model is created using 3D modeling software and then sent to the printer. The printer uses a UV light source, such as a laser or a projector, to selectively cure the liquid resin, solidifying it layer by layer to create the final object.
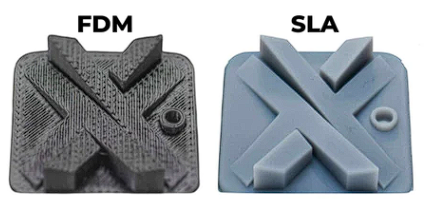
Resin 3D printing is known for its ability to produce high-resolution, detailed, and smooth-surfaced objects with complex geometries. It is commonly used in a variety of applications, including jewelry making, dental prosthetics, product design, and more.
However, resin 3D
 printing can be more expensive than other types of 3D printing, and the liquid resin can be messy and require proper handling and disposal. Additionally, the resin can emit fumes during printing that may be harmful if inhaled, so it is important to take proper safety precautions when using a resin 3D printer.
printing can be more expensive than other types of 3D printing, and the liquid resin can be messy and require proper handling and disposal. Additionally, the resin can emit fumes during printing that may be harmful if inhaled, so it is important to take proper safety precautions when using a resin 3D printer.
After every print the parts must be cleaned of all uncured materials and then finally cured via the materials required post processed. Most require UV curing to finish hardening the material while others may require a specialized heated chamber.
Lastly, the material properties of resin 3D printing material is not as durable as FDM printing. The majority of resin materials are known to be brittle and degrades in UV light.
Resin 3D Printing like all additive manufacturing technique simplifies the geometry into layers using software known as "Slicers" to control every detail of the 3D Printer as it is printing the object. It takes the initial geometry supplied by the users mesh file and slices it (Generally Verticall) into a predetermined height for each slice. These slices for resin 3D printing can varry between .01mm (.003in)-.05mm (.04in) per layer.
Resin printers come in a smaller variety of sizes and material capibilities then compared to FDM 3D Printing. The print materials are similiar to those found in FDM printing but are rather in a resin form with different qualities per material. The print sizes are genrally on the smaller side for a consumer mahcine ranging from only 4"x4"x4" to up to 10"x10"x10" for most consumer grade machines.
Commerical/ Industrial grade machines are genrally much larger, faster, and more accurate then their consumer counter parts. Some are capable of utlizing high power lasers to cure much more durable materials which incrases cost but increases possible parts creation.
| Layer Line Heights | 0.01mm (.0003in) - .05mm (.03in) |
| Accuracy | +/- .005mm (.0002in) - +/- .02mm (.0007in) |
| Print Speeds | .5-20s per Layer (Depends on Printer and Material) |
This site was created with the Nicepage